Bitter Melon Market Summary


Image: Jo Theera/Shutterstock.com
Bitter Melon Market Overview
Bitter melon (Momordica charantia) is a member of the Cucurbitaceae family, which also includes cucumbers, squash, watermelon, and muskmelon. In different parts of the world, this commodity is called bitter gourd, bitter squash, balsam apple, bitter cucumber, karalla, balsam pear, and a number of other names. Ranging from 5 to 12 inches long (depending on variety), bitter melon resembles a wrinkled cucumber. It is generally picked when green, though the fruit will eventually turn yellow or orange as it ripens. Inside is a white layer of pulp with reddish-pink seeds, but the fruit is not eaten raw. A subtropical to tropical melon, it is one of the most popular vegetables in Southeast Asia. Native to China and India, the fast-growing, climbing vine crop is widely produced throughout Asia, Africa, South America, Mexico, and the Caribbean. To a lesser degree, bitter melon is grown as a specialty vegetable in subtropical regions of the United States, including Florida, Hawaii, and California. While technically a fruit, bitter melon is eaten as a vegetable and incorporated into dishes to add a delightfully acidic flavor. Considered the most bitter of all fruits, it is often soaked in water to diminish its bitterness and then boiled, fried, curried, steamed, or pickled. The curcubit is commonly used in Caribbean and Asian-inspired cuisine, including stew, soup, and stir fry meals. Hailed for its medicinal value, this nutrient-rich fruit has attracted the attention of doctors and scientists across the globe. High in iron, calcium, potassium, beta carotene, folate, and Vitamin C, it is also being studied for potential treatment of infectious diseases, diabetes, skin conditions, and other ailments.
Bitter Melon Types & Varieties
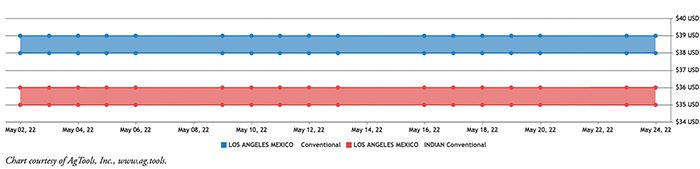
There are two primary types of bitter melon: Chinese and Indian. The Chinese melon is wider and longer, usually 8 to 12 inches in length. Rounded at the ends, this variety has light green skin with smooth, wart-like bumps. The Indian variety is smaller with pointy ends and rough, dark green skin featuring sharp ridges.Bitter Melon Cultivation
Bitter melon is a warm weather crop that thrives in daytime temperatures between 75 and 80°F. In the tropics, the gourd can be planted year-round as long as crops are properly irrigated during drier months. The plant does best in lowland areas to altitudes of up to 3,200 feet. While typically cultivated in the field, it can also be grown in a greenhouse. The plant can be transplanted or grown from seeds, which require warm and moist conditions to germinate. Soon after germination, the plant will grow three to four leaves. Once leaves appear, the plant’s vines will sprout tendrils and start climbing. These fast-growing vines can extend to more than 15 feet long with numerous branches. For this reason, crops typically require a trellis support system after 4 to 6 feet in height. Bitter melon prefers well-drained, sandy or silty loam. If grown in wet conditions, bacterial and fungal wilt can have a negative impact on plant health and fruit growth. Rows should be generous at 5 to 6 feet apart with 3 to 5 feet between individual plants. Depending on growing region, fruit will be ready for harvest 50 to 70 days after seeding. When plants are transplanted, the fruit will grow more quickly. Bitter melon is picked by hand and requires close attention during harvest time. Because the fruit develops rapidly, it must be harvested frequently, usually every 2 to 3 days.